This post is a summary post of the in-depth dive the ODX research team did on Stress and Biomarkers.
CLICK HERE to access our 11-part series on "Stress Biomarkers and Consequences".
Any overview of stress will be understated but there are some basics we should all recognize about stress and its effects on our bodies.
Stress is everywhere, how we cope with it determines whether it makes us sick. The general response to stress is the acute "fight or flight" mode which gets our bodies ready to fight an adversary or run away to save our skins. Blood pressure, heart rate, and blood glucose increase while immune and gastrointestinal function decrease. As you can imagine, we can't thrive in this heightened survival mode for very long without consequences.
Once the threat has passed, then we should go into a more relaxed, "rest and digest" phase. However, many people remain in the chronic heightened alert phase of stress which increases the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and gastrointestinal disorders.
We may even transition into the exhaustion phase with fatigue, burnout, decreased ability to function effectively, and even post-traumatic stress disorder.
It is very important to recognize potential stressors and address them as early as possible.
There are many biochemical reactions that occur in the body during stress. Many of these changes help the body to fight a stressor but they become harmful if prolonged:
Managing stress can be an art. You must be aware of your stressors, recognize associated changes in your body, and make a conscious effort to counteract the effects of stress. Simple stress management techniques include:
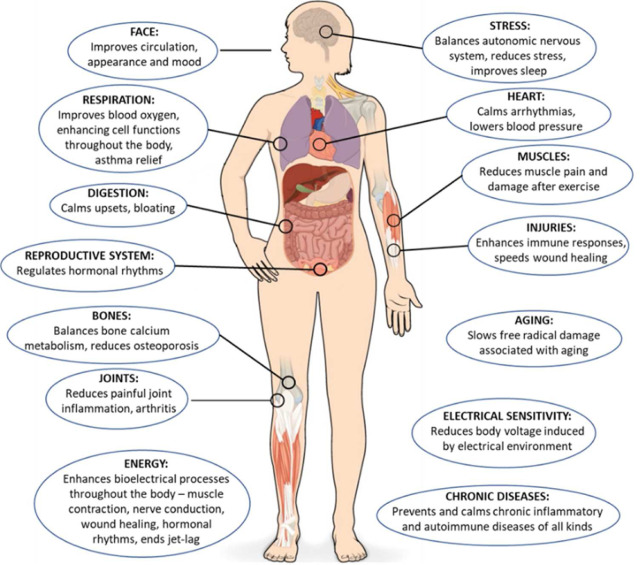
Source: Menigoz, Wendy et al. “Integrative and lifestyle medicine strategies should include Earthing (grounding): Review of research evidence and clinical observations.” Explore (New York, N.Y.) vol. 16,3 (2020): 152-160. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2019.10.005 [R] This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license. ([R])
The stress response requires micronutrients, macronutrients, and energy to sustain it. It is especially important to eat a healthy diet in times of stress, one that includes:
Since stress is just about everywhere, resilience to stress must be everywhere as well. Identifying stressors is the first step in meeting stress head-on. Then, you must take active measures to counteract stress and support health. Your life could depend on it!
Nutrition support, exercise, and mindfulness are the foundations for healthy stress management and recovery… these should be incorporated into your daily routine.
This post is a summary post of the in-depth dive the ODX research team did on Stress and Biomarkers. Click below to download our whitepaper: