Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: In sync with zinc
Dicken Weatherby, N.D. and Beth Ellen DiLuglio, MS, RDN, LDN
Researchers reviewed a number of studies utilizing nutrition or phytochemical prevention or intervention for COVID-19
The ODX COVID-19 Series
- COVID-19: The pandemic that has become endemic
- COVID-19: Overlapping risk factors and chronic disease
- Nutritional status COVID-19: A covert factor in disease susceptibility
- COVID-19: Blood chemistry biomarker patterns - Clues and patterns lurking just under the surface
- COVID-19: Blood chemistry biomarker patterns - Down the research rabbit hole
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Neutrophils
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Albumin
- COVID-19: BloodBiomarkers - Cytokines
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Interleukin-6
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Interleukin-10
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Vitamin C
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Vitamin D
- COVID-19: Blood Biomarkers - Zinc
- Biomarker characteristics and blood type - help sharpen the COVID-19 clinical picture
- COVID-19: Initial indications and conventional interventions
- COVID-19: Long-term risk reduction - Naturopathic, functional medicine, and nutrition-based approaches to prevention
- A healthy diet is primary prevention for COVID-19
- You should have a gut feeling about COVID-19
- Beyond dietary food patterns…plant-based compounds may mitigate COVID-19 risk
- Targeted nutrition support in the battle against COVID-19
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: Armed with vitamin C
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: In sync with zinc
- Targeted nutrition support in COVID-19: Micronutrients and phytonutrients are important players
- Optimal Takeaways for improving immunity and reducing susceptibility to COVID-19
- Optimal - The Podcast: Episode 8 -Blood Biomarkers and Risk Factors for COVID-19 and its Comorbidities
The most promising nutritional and phytochemical compounds being:[i]
- Catechin gallate and gallocatechin gallate
- Elderberry
- Fiber
- Forsythoside
- Melatonin
- Polyphenols
- Probiotics
- Propolis
- Quercetin
- Selenium
- Vitamins A, C, E, D
- Zinc
Effects of several nutrients on aspects of COVID-19 infection. ↑: increase, ↓: decrease
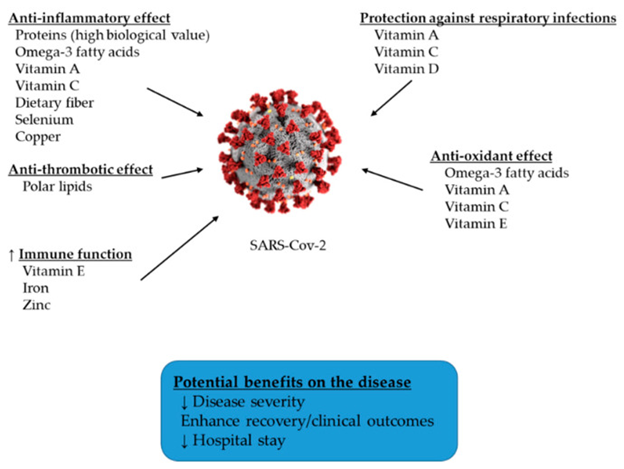
Source: Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589
Recommended intakes of certain nutrients with key roles in disease susceptibility and the maintenance of an adequate immune function. [ii]
|
Nutrient |
Immune Function |
Recommendation |
|
|
Healthy Individuals |
Diseased/Infected Patients |
||
|
Vitamin C |
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers |
200 mg/day |
1–2 g/day |
|
Vitamin D |
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers |
2000 IU/day (50 µg/day) |
10,000 IU during few weeks, followed by 5000 IU (until 25–hydroxyvitamin D concentrations rise above 40–60 ng/mL (equivalent to 100–150 nmol/L)) |
|
Vitamin E |
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers |
15 mg/day (RDA) |
200 IU/day |
|
Selenium |
Differentiation, and functioning, of innate immune cells |
50 µg/day |
Up to 200 µg/day |
|
Zinc |
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers. |
Men: 8 mg/day |
Zinc lozenges: over 75 mg/day administered within 24 h (divided into 6–8 doses, each separated by 2–3 h when awake) |
|
Iron |
Maintenance of functional and structural integrity of mucosal cells in innate barriers |
Men: 8 mg/day |
Ferrous iron salts (ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate): 60 mg Fe/day (taken with food to avoid gastric discomfort) |
|
Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA + DHA) |
Conversion to specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) such as, protectins, resolvins and maresins to relieve the inflammation and enhance lung injury |
250–300 mg/day of EPA + DHA |
1500–3000 mg/day EPA + DHA |
|
Multivitamin supplements including vitamins (A, B6, B12, C, D, E and folate) and trace elements (Zn, Fe, Se, Mg and Cu) |
Support of the cells and tissues of the immune system overall |
Supplying nutrient requirements according to the 100% RDA for age and gender |
|
Source: Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589
An entire array of micronutrients factors into the body’s susceptibility to and ability to fight against COVID-19. Each nutrient is a cog in the wheel and should not be overlooked in order to optimize health during this perpetually rampant pandemic.
Next Up - Optimal Takeaways for improving immunity and reducing susceptibility to COVID-19
Research
[i] Ayseli, Yasemin Ipek, et al. "Food policy, nutrition and nutraceuticals in the prevention and management of COVID-19: Advice for healthcare professionals." Trends in Food Science & Technology (2020).
[ii] Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo et al. “Key Aspects in Nutritional Management of COVID-19 Patients.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 9,8 2589. 10 Aug. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcm9082589






